Understanding Split Phase Motors
Split phase motors are widely used in various electrical appliances, such as washing machines, compressors, vacuum cleaners, table drills, and pumps. Their popularity stems from their balance of performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. This post explores their operation, advantages, and components, with a focus on their practical applications.
Why Are Split Phase Motors Popular?
Split phase motors offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice for many applications:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Good Starting Torque | Provides sufficient power to start most small and medium loads efficiently. |
| Moderate Efficiency | Offers reasonable energy efficiency for household and light industrial use. |
| Moderate Cost | Affordable, making them suitable for widespread usage. |
Power Ratings:
Typically range from 1/20th Hp to ¾ Hp, with some models available up to 1.5 Hp.

Construction of Split Phase Motors
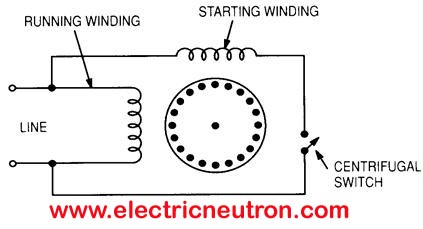
Split phase motors consist of two windings:
- Primary Winding (Running Winding):
Responsible for maintaining continuous motion after the motor starts. - Secondary Winding (Starting Winding):
Provides the necessary torque to initiate motor rotation.
Centrifugal Switch:
A centrifugal switch is used to disconnect the starting winding once the motor reaches a certain speed.
Operation of Split Phase Motors
The motor operates in the following sequence:
- Startup Phase:
- Both the running winding and starting winding are connected in parallel to the power supply.
- The starting winding generates the initial torque required to start the motor.
- Reaching Operating Speed:
- As the motor accelerates, it approaches 70% of synchronous speed.
- At this point, the centrifugal switch disconnects the starting winding.
- Running Phase:
- The motor continues to operate using only the running winding, which is optimized for efficiency and sustained motion.

Role of the Centrifugal Switch
The centrifugal switch plays a critical role in the motor’s operation:
- Purpose: Disconnects the starting winding when the motor reaches 70% of its synchronous speed.
- Types of Issues:
- Sticks Open: The switch fails to close, preventing the starting winding from engaging.
- Sticks Shut: The switch fails to open, causing the starting winding to remain active, potentially overheating.

Applications of Split Phase Motors
Split phase motors are versatile and find applications in various household and light industrial devices:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Washing Machines | Provides reliable torque to handle drum rotation. |
| Compressors | Powers small air compressors efficiently. |
| Vacuum Cleaners | Drives high-speed fans for effective suction. |
| Table Drills | Ensures smooth and precise drilling operations. |
| Pumps | Powers water pumps for domestic and light industrial use. |
Advantages and Limitations
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Simple design and affordable construction. | Limited to applications requiring moderate torque. |
| Suitable for applications with fixed speed. | Not ideal for high-efficiency applications. |
| Reliable for household and small industrial uses. | Cannot handle frequent starts/stops or heavy loads. |
Conclusion
Split phase motors are a dependable and cost-effective solution for many household and light industrial applications. By leveraging their good starting torque and moderate efficiency, they meet the needs of a wide range of devices. However, understanding their operation, particularly the role of the centrifugal switch, is crucial to maintaining their performance and extending their lifespan.
For optimal use, select a motor that matches the application’s load and operating conditions. If you encounter issues with the centrifugal switch or windings, consult a professional technician for troubleshooting and repair. Stay tuned for more insights into motor technologies and applications!
It is a single phase motors are widely used in electrical appliances such as washing machines, some compressors,vacuum cleaner, table drill, pump, etc.
